The human body is an incredible machine and a key component of its function is oxygen. Oxygen is required for all the essential biological processes in our bodies, from breaking down food to powering our muscles. A critical aspect of our oxygen intake is oxygen saturation, which is one of the most important indicators of our overall health and well-being. This essay will help you grasp the underlying concept of oxygen saturation and its significance for our bodies. We’ll also guide you through the process of using an oximeter, a handy device for tracking your oxygen levels, and discuss common challenges and solutions tied to measuring oxygen saturation.
Understanding Oxygen Saturation
Understanding Oxygen Saturation: The Life-Sustaining Element
The role of oxygen in our bodies is a fundamental part of human survival. It powers every cell and organ in our body, which explains why “oxygen saturation” might be a term you’ve encountered. So, what is oxygen saturation, and why is it so essential to our well-being?
The Concept of Oxygen Saturation
Oxygen saturation (SpO2) refers to the extent to which oxygen is saturating or filling our red blood cells. These cells are responsible for carrying oxygen from the lungs to the rest of the body’s tissues and organs.
Basically, if we imagine our bloodstream as a highway, the red blood cells are the delivery trucks, and oxygen molecules are the goods being transported. Oxygen saturation then tells us how fully loaded these trucks are – showing the percentage of the hemoglobin in red blood cells currently carrying oxygen.
The Importance of Oxygen Saturation
Given that oxygen is vital for body cells’ metabolism, maintaining an appropriate level of oxygen saturation is crucial. It helps in ensuring that every part of the body has access to the oxygen it needs for proper functioning. Inadequate oxygen levels can lead to cellular dysfunction or even cell death.
If the body’s oxygen saturation levels drop too low, it can lead to hypoxemia, a condition that can cause tissue damage and potentially life-threatening health complications.
Normal and Abnormal Oxygen Saturation Levels
Healthy individuals under normal conditions have an oxygen saturation level between 95% – 100%. Typically, healthcare professionals consider anything under 90% as abnormal or low. This condition, known as hypoxemia, can cause symptoms such as shortness of breath, rapid heart rate, sweating, wheezing, or even cyanosis, where the skin, lips, or fingernails turn blue.
On the other hand, abnormally high levels of oxygen saturation exceeding 100% are also unhealthy. This rare condition, known as hyperoxemia, could lead to oxygen toxicity, damaging cell tissues due to excessive oxygen levels. It’s often caused by breathing air or gas with a high concentration of oxygen for prolonged periods, like in deep-sea diving or some medical treatments.
While these are general guidelines, the range of normal oxygen saturation can vary depending on age, health status, ambient temperature, altitude, and other factors. Therefore, it’s essential to consult with healthcare professionals for personalized advice.
As a takeaway, understanding oxygen saturation provides valuable insights into your health, especially respiratory health. In today’s world, where even wearable technology like smartwatches can monitor oxygen saturation, understanding this concept empowers you to take better control of your health.
Remember, it’s not just about breathing—but making sure your body is making the most effective use of that breath!
How to Use an Oximeter
Understanding Oximeters
An oximeter, also known as a pulse oximeter, is a device widely used in the healthcare sector that measures the level of oxygen saturation or the oxygen levels in the blood. It is a non-invasive tool that indicates the oxygen-carrying capacity of the hemoglobin in the bloodstream. The oximeter is typically used to assess the cardiorespiratory health of a patient, thereby allowing healthcare professionals to make essential clinical decisions.
Preparing the Oximeter
- Remove the oximeter from its case or box and ensure it is clean and ready for use. Any presence of dust or dirt can impact the accuracy of the readings.
- Most oximeters function with regular batteries. Check and ensure that the oximeter is sufficiently powered. Replace the batteries if necessary.
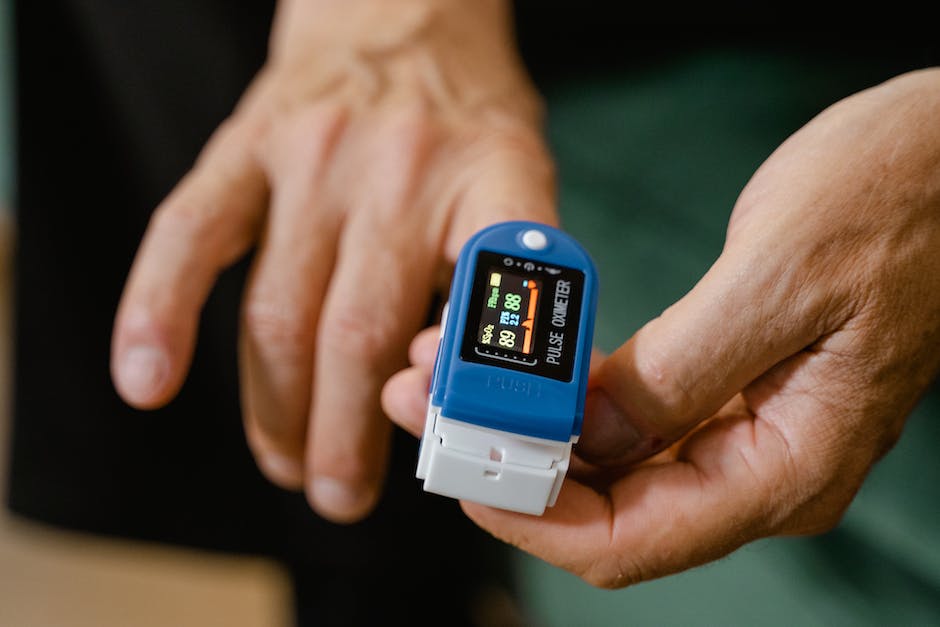
- Evaluate the device’s display screen to ensure it’s clear and easy to read. The information shown typically includes oxygen saturation (SpO2, displayed as a percentage), pulse rate (measured in beats per minute), and a waveform graph or bar graph representing each pulse beat.
How to Use the Oximeter
- Open the oximeter by pressing or squeezing a button or section that allows it to open like a clothespin.
- Carefully place your index or middle finger into the slot of the device, making sure your fingertip is positioned under the red light. Your nail should face upward towards the light source.
- Firmly close the oximeter ensuring the device fits snugly, but not too tightly that you feel discomfort or pain.
- Press the “on” switch of the device to begin capturing your readings.
- Sit quietly while the oximeter takes your reading. It’s best to not make unnecessary movements as this can interfere with the results.
- Generally, you’ll see your readings in about 15 to 30 seconds.
Interpreting the Oximeter Readings
- The SpO2 reading is shown as a percentage. In healthy individuals, this reading typically ranges between 95% to 100%.
- Any SpO2 reading lower than 90% is considered abnormal and indicates a low level of oxygen in the blood. This condition, known as hypoxemia, requires medical attention.
- The pulse rate displayed on the oximeter corresponds to the rate at which your heart is beating. Again, this rate varies from person to person depending on their overall health and activity level. However, for an adult at rest, a normal pulse rate falls between 60 to 100 beats per minute.
Remember, while an oximeter provides valuable information about your oxygen saturation levels, it does not measure CO2, the carbon dioxide levels. So, if you experience symptoms such as difficulty in breathing, don’t just rely on the oximeter readings, seek immediate medical attention. Also, make sure you periodically validate the accuracy of your oximeter with professional medical devices or under professional medical supervision.
Learning how to use an oximeter can help you monitor your health more carefully, especially if you’re dealing with chronic lung diseases, heart conditions, or Covid-19.
Common Challenges & Tips
Troubleshooting Problems with the Oximeter
Measuring oxygen saturation isn’t always a straight-forward process. You may come across hiccups with the oximeter itself. Common issues include the device not turning on, not picking up a signal, or providing inconsistent readings.
The first step in troubleshooting is to check the basics. Confirm if the batteries are charged and inserted correctly. A dislodged or dead battery could easily be the reason behind the oximeter not turning on or working properly.
Next, check the finger placement. The finger should be placed correctly and snug into the probe, ensuring the light from the oximeter passes through the finger.
Finally, ensure that the oximeter is calibrated correctly. An out-of-calibration oximeter may provide inaccurate readings. If you’re uncertain how to calibrate your device, refer to the manufacturer’s instructions or get support from a healthcare professional.
Should the device still not function as it should, consider getting it examined by a professional or replaced.
How Movement May Affect Readings
Movement is a significant factor that can influence the accuracy of the oxygen saturation reading. Constant motion causes the oximeter to pick up the movement and interpret it as a pulse, potentially leading to inaccurate results.
The best way to overcome this challenge is to stay as still as possible during the measurement. If you’re measuring the saturation level on someone else, encourage them to keep their hand steady and avoid talking or other movements. Also, placing the hand on a stable surface can help minimize movement and ensure accurate results.
How Lighting May Affect Readings
You may not realize this, but the lighting environment can also impact the readings. Strong ambient light, especially sunlight, can interfere with the sensor’s ability to accurately measure oxygen saturation levels.
To mitigate this, try to measure oxygen saturation in a well-lit indoor setting, ideally away from direct sunlight. If outdoors, use your body to cast a shadow over the device or cover it with a cloth to block out the excess light.
How Body Temperature May Impact Readings
Another common issue is changes in body temperature, which can affect your blood vessels and consequently impact the readings. If you’re cold, your blood vessels might constrict, making it difficult for the oximeter to get a reading.
To get the most accurate reading possible, make sure your hands are not too cold or hot before taking a measurement. You can warm your hands by rubbing them together or wrapping them in a blanket for a few minutes if necessary.
Conclusion
By being aware of these potential challenges and knowing how to overcome them, you can obtain more reliable and consistent readings while measuring oxygen saturation. Remember that if you’re unsure or your readings consistently seem off, it’s best to seek advice from a healthcare professional.
By gaining an understanding of oxygen saturation, its importance and how to measure it, we can proactively manage and monitor our health. The correct use of an oximeter can provide a quick, non-invasive, and effective way to gauge our oxygen levels – it’s a remarkable tool that may save lives. However, understanding the potential complications and learning ways to circumvent them is crucial for accurate readings. Our hope is that this information equips you with a better understanding of your body’s oxygen needs, the importance of maintaining healthy oxygen levels and how to tackle the most common issues in oxygen measurement.

Rakib Sarwar is a seasoned professional blogger, writer, and digital marketer with over 12 years of experience in freelance writing and niche website development on Upwork. In addition to his expertise in content creation and online marketing, Rakib is a registered pharmacist. Currently, he works in the IT Division of Sonali Bank PLC, where he combines his diverse skill set to excel in his career.