Hydrogen has a density of about 0.08988 grams per liter at standard temperature and pressure. It is the lightest and most abundant element in the universe.
Hydrogen is a colorless, odorless gas that plays a crucial role in various industries. Its low density makes it a preferred choice for applications requiring lightweight materials. Hydrogen is commonly used in fuel cells, which convert chemical energy into electricity with high efficiency.
It also serves as a key reactant in the production of ammonia for fertilizers. The element’s lightweight nature and abundance make it a promising candidate for future energy solutions. Researchers are continually exploring hydrogen’s potential in reducing carbon emissions and promoting sustainable energy practices.
Credit: neutrons.ornl.gov
Introduction To Hydrogen
Hydrogen is the lightest and most abundant element in the universe. It plays a crucial role in many scientific fields. Understanding hydrogen is key to many technologies.
Discovery And History
Hydrogen was first discovered by Henry Cavendish in 1766. He realized that hydrogen was a distinct gas. Cavendish called it “inflammable air” because it burned easily.
In 1783, Antoine Lavoisier named the element “hydrogen”. The name means “water-former” in Greek. Lavoisier discovered that hydrogen produces water when burned.
Hydrogen In The Periodic Table
Hydrogen is the first element in the periodic table. It has an atomic number of 1. This means it has one proton and one electron.
| Property | Value |
|---|---|
| Symbol | H |
| Atomic Number | 1 |
| Atomic Mass | 1.008 |
Hydrogen is unique because it can exist as a gas, liquid, or solid. It has many applications in science and industry.
Hydrogen is a key part of water (H2O). It is essential for life and many chemical processes. Its study helps us understand the universe better.
Physical Properties Of Hydrogen
Hydrogen is the lightest and most abundant element in the universe. It has unique physical properties that make it fascinating. Understanding these properties helps us comprehend its behavior and applications.
Atomic Structure
Hydrogen has a simple atomic structure. It consists of one proton and one electron. This makes it the simplest element. In its most common form, hydrogen has no neutrons.
The atomic number of hydrogen is 1. This means it has one proton in its nucleus. The electron orbits around the nucleus. This simplicity gives hydrogen unique chemical properties.
State And Density
Hydrogen can exist in different states. These states are gas, liquid, and solid. At room temperature, hydrogen is a gas.
The density of hydrogen gas is very low. It is about 0.08988 grams per liter. This makes hydrogen much lighter than air. This property is why hydrogen was used in balloons.
When cooled to very low temperatures, hydrogen becomes a liquid. The density of liquid hydrogen is higher than its gaseous state. It is about 70.85 grams per liter. This makes it useful for storage and transport.
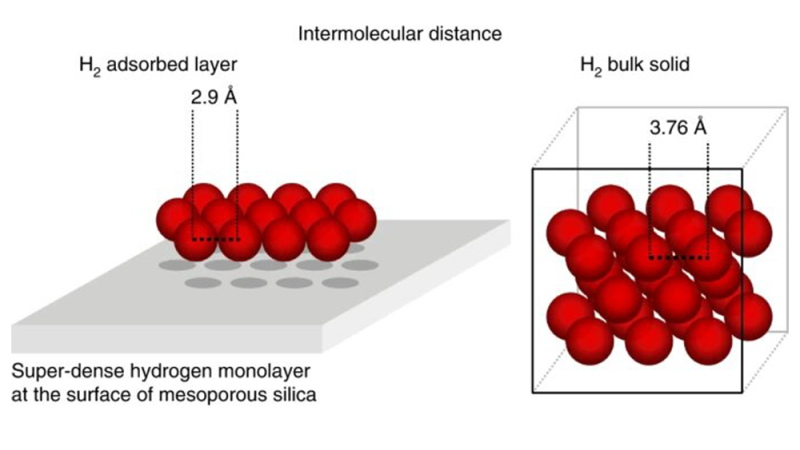
In its solid state, hydrogen has an even higher density. Solid hydrogen forms under extreme pressure and low temperature. It is used in advanced scientific research.
Hydrogen Density Table
| State | Density (grams per liter) |
|---|---|
| Gas | 0.08988 |
| Liquid | 70.85 |
| Solid | Varies with pressure |
Hydrogen’s low density in its gaseous state makes it ideal for certain applications. Its higher density in liquid form makes it useful for different purposes. Understanding these properties helps us use hydrogen effectively.
Measuring Hydrogen’s Density
Hydrogen is the lightest and simplest element in the universe. Despite its simplicity, measuring its density presents unique challenges. Scientists use various methods to determine how dense hydrogen is.
Methods And Techniques
Several methods are used to measure hydrogen’s density. These methods include:
- Gravimetric Method: This method measures the mass of hydrogen gas.
- Volumetric Method: This technique measures the volume of hydrogen at a known pressure and temperature.
- Acoustic Method: This method uses sound waves to determine the density of hydrogen.
Each method has its own advantages and is chosen based on the situation.
Challenges In Measurement
Measuring the density of hydrogen comes with unique challenges. Hydrogen atoms are very small and light. This makes it difficult to measure accurately.
Here are some common challenges:
- Leakage: Hydrogen gas can easily escape from containers.
- Purity: Impurities can affect measurement accuracy.
- High Reactivity: Hydrogen can react with materials, altering measurements.
Overcoming these challenges requires specialized equipment and techniques.
| Method | Advantages | Challenges |
|---|---|---|
| Gravimetric | Direct mass measurement | Requires precise scales |
| Volumetric | Can measure large samples | Temperature control needed |
| Acoustic | Non-intrusive | Requires sound calibration |

Credit: commons.wikimedia.org
Applications Of Hydrogen
Hydrogen is a versatile element with many applications. It is the lightest and most abundant element in the universe. Understanding how dense hydrogen is helps us see its potential uses.
Industrial Uses
Hydrogen plays a crucial role in various industries. Here are some key applications:
- Ammonia Production: Hydrogen is essential for making ammonia. Ammonia is then used to produce fertilizers.
- Petroleum Refining: Hydrogen helps remove sulfur from crude oil. This process makes cleaner fuels.
- Metal Processing: Hydrogen is used to reduce metal ores. This helps in extracting pure metals.
- Glass Manufacturing: Hydrogen helps create a controlled atmosphere. This is vital for making high-quality glass.
Hydrogen As Fuel
Hydrogen has a significant role in the energy sector. Here are some ways it is used as fuel:
- Fuel Cells: Hydrogen fuel cells generate electricity. They are used in cars, buses, and even buildings.
- Hydrogen Combustion: Hydrogen can be burned as a fuel. This process produces only water as a byproduct.
- Energy Storage: Hydrogen can store energy from renewable sources. This energy can be used later when needed.
Here is a table summarizing the key applications of hydrogen:
| Application | Industry |
|---|---|
| Ammonia Production | Agriculture |
| Petroleum Refining | Energy |
| Metal Processing | Manufacturing |
| Glass Manufacturing | Manufacturing |
| Fuel Cells | Energy |
| Hydrogen Combustion | Energy |
| Energy Storage | Energy |
Future Prospects
Hydrogen is a light and abundant element. It holds promise for future energy solutions. Its density impacts its storage and transportation. Let’s explore future prospects.
Innovations In Hydrogen Technology
Innovations in hydrogen technology are accelerating. Scientists are developing better storage methods. Solid-state storage is one exciting area. It involves storing hydrogen in metal hydrides. This method increases safety and efficiency.
Another innovation is liquid organic hydrogen carriers (LOHCs). LOHCs store hydrogen in liquid form. This method is safer and easier to transport. It also reduces the need for high-pressure tanks.
Fuel cells are also improving. They convert hydrogen into electricity. Fuel cells are getting smaller and more efficient. This makes them ideal for cars and portable devices.
Impact On Energy Sector
Hydrogen can transform the energy sector. It can replace fossil fuels. This reduces carbon emissions. Hydrogen is a clean and renewable energy source.
The use of hydrogen in power plants is growing. Hydrogen can be burned to produce electricity. This is cleaner than burning coal or natural gas.
Transportation is another key area. Hydrogen-powered vehicles produce zero emissions. They are more efficient than gasoline cars. Hydrogen refueling stations are expanding globally.
Industrial applications are also benefiting. Hydrogen is used in metal refining and chemical production. Its clean properties make it ideal for these processes.
| Application | Benefits |
|---|---|
| Power Plants | Cleaner energy production |
| Transportation | Zero emissions |
| Industrial Applications | Cleaner processes |
Credit: www.researchgate.net
Frequently Asked Questions
What Is The Density Of Hydrogen?
Hydrogen has a density of 0. 08988 grams per liter at standard temperature and pressure.
How Does Hydrogen’s Density Compare To Air?
Hydrogen is much lighter than air, approximately 14 times less dense.
Can Hydrogen’s Density Change?
Yes, hydrogen’s density changes with temperature and pressure conditions.
Why Is Hydrogen Less Dense Than Other Gases?
Hydrogen has the smallest atomic mass, making it the least dense of all gases.
What Factors Affect Hydrogen’s Density?
Temperature and pressure significantly affect the density of hydrogen gas.
Is Hydrogen’s Density Important For Storage?
Yes, understanding hydrogen’s density is crucial for efficient storage and transportation.
Conclusion
Understanding hydrogen’s density is crucial for various applications. It’s the lightest element, making it unique for energy storage. Hydrogen’s low density poses both challenges and opportunities. As we explore sustainable solutions, hydrogen’s role becomes more significant. Stay informed about hydrogen to leverage its potential benefits in future technologies and energy solutions.
