To measure the Floor Area Ratio (FAR) for building projects, you first need to know the formula. FAR is the total building floor area divided by the area of the plot.
This ratio helps in understanding the density and intensity of the land use. Understanding how to measure FAR is vital for architects, builders, and city planners. It impacts the design and functionality of buildings. FAR regulations vary across cities and countries.
These rules ensure balanced development, preventing overcrowding. Knowing how to calculate FAR helps in planning building projects that comply with local zoning laws. It ensures efficient use of land while considering community needs. In this post, we will explain the steps to measure FAR accurately. This knowledge is essential for anyone involved in construction and urban planning.
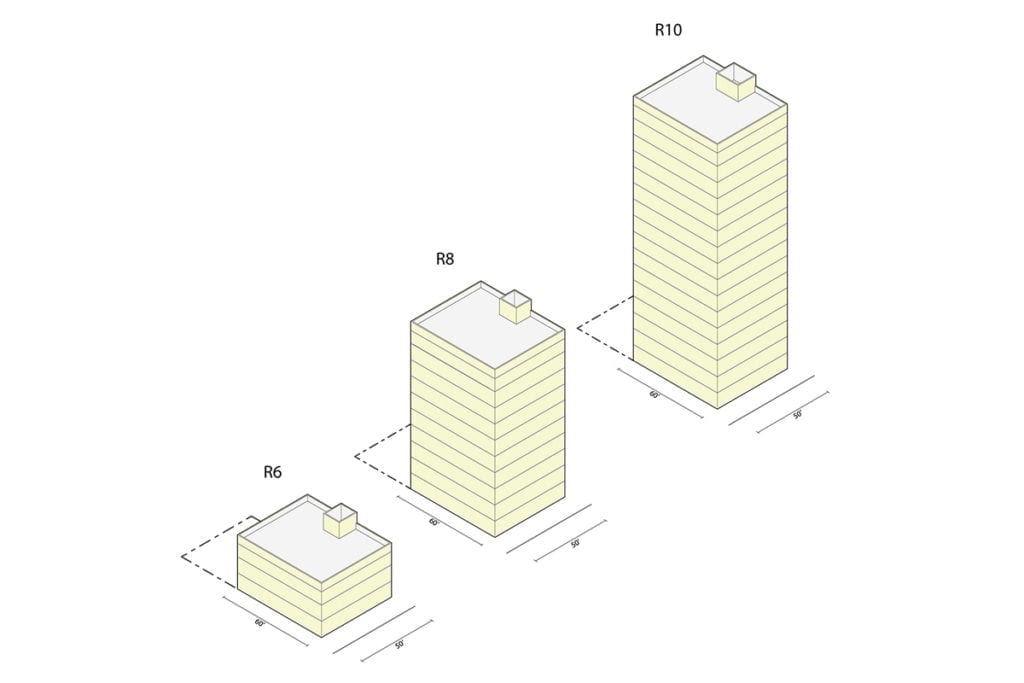
Credit: fontanarchitecture.com
Introduction To Floor Area Ratio
Hey friends, today let’s talk about a crucial factor in building projects – Floor Area Ratio (FAR). If you are planning a building project, understanding FAR is essential. It helps you know how much floor space you can build on a piece of land. This concept is simple, but very important in urban planning.
Definition Of Far
First, let’s define what Floor Area Ratio is. FAR is the ratio of a building’s total floor area to the size of the piece of land upon which it is built. It is usually expressed as a decimal number. For example, if you have a land area of 1,000 square meters and the total floor area of your building is 2,000 square meters, the FAR would be 2.0. Simple, right?
Let’s break it down:
- Land Area: The total area of the plot of land.
- Total Floor Area: The sum of the floor areas of all the floors in the building.
So, the formula looks like this:
FAR = Total Floor Area / Land Area
Importance In Urban Planning
Now, why is FAR important in urban planning? Well, it helps city planners control the density of buildings. This means they can decide how many buildings can be constructed in a specific area. This is crucial for managing resources like water, electricity, and roads. Imagine a city without any planning. It would be chaotic, right?
Here are some key reasons why FAR matters:
- Prevents Overcrowding: By controlling the amount of floor space, cities can prevent overcrowding.
- Ensures Adequate Light and Air: Proper FAR ensures buildings are not too close together, which allows for enough light and air.
- Maintains Aesthetic Appeal: It helps maintain the look and feel of a neighborhood.
I recently talked to an architect friend who emphasized how FAR is like a guide. It helps architects and builders know the limits and possibilities of a project. Without it, you might end up with buildings that don’t fit well in their surroundings.
So, understanding FAR is not just about numbers. It’s about creating a balanced, well-planned environment for everyone. And the good news? It’s pretty easy to understand and apply in your projects!
Regulatory Framework
Hey friends, understanding the Regulatory Framework is crucial when measuring Floor Area Ratio (FAR) for building projects. These rules and guidelines ensure that buildings are safe and suitable for their environments. Let’s dive into the key components: zoning laws and local building codes.
Zoning Laws
First up, let’s talk about zoning laws. These laws decide what can be built and where. Think of it like a map for builders. Different areas have different rules. For example:
- Residential zones: Where houses and apartments can be built.
- Commercial zones: Where shops and offices are allowed.
- Industrial zones: Where factories and warehouses can be constructed.
Knowing your zone is like having a blueprint. It tells you the basics of what you can do. If you want to build a tall building in a residential area, zoning laws might stop you. Always check the zoning laws first. They are the starting point for measuring FAR.
Local Building Codes
Next, we have local building codes. These are rules set by your local government. They make sure buildings are safe and practical. Building codes cover a lot of details, such as:
- Height limits
- Minimum room sizes
- Fire safety measures
- Accessibility requirements
Think of building codes as a rulebook. They give you the specifics. For instance, if you want to build an apartment, there are rules about how big the windows need to be. Or how many exits are needed in case of fire. These codes ensure everything is up to standard.
Combining zoning laws and building codes gives you a clear picture. They work together to guide your project. Always start here when measuring FAR. It saves time and avoids mistakes. Remember, understanding these rules is not just about following the law. It’s about making buildings safe and suitable for everyone.
Calculating Floor Area
Calculating the floor area ratio (FAR) is essential for building projects. It helps determine the allowable building size on a given lot. To start, you need to measure the floor area. This includes the building footprint and any multi-story spaces.
Measuring Building Footprint
The building footprint is the area covered by the structure at ground level. Measure the length and width of the building. Multiply these numbers to get the footprint area. If the building has a unique shape, break it into smaller rectangles. Measure each rectangle and sum their areas.
Including Multi-story Spaces
Multi-story spaces add to the total floor area. Measure each floor separately. Include basements, mezzanines, and attics if they are usable spaces. Multiply the footprint of each floor by the number of stories. Add these numbers together for the total floor area.
Determining Lot Area
Hey friends, today let’s talk about something important for your building projects – the Floor Area Ratio (FAR). To get started, we need to determine the lot area. This is the first step in calculating your FAR. It’s easier than you might think. Let’s break it down together.
Property Boundaries
First, you need to find out the exact boundaries of your property. This is where your lot area begins. Think of it as finding the edges of a puzzle piece. You need to know the shape and size of your land. Here are some steps to help you:
- Check your property deed. This document shows your property lines.
- Look at a survey map. This map is like a blueprint of your land.
- Measure the dimensions. Use a tape measure to find the length and width of your lot.
Got it? Great! Now you know where your property starts and ends.
Exclusions And Inclusions
Next, let’s talk about what to include and what to exclude. Not everything on your land counts towards your lot area. For example, public streets or sidewalks next to your property are usually not part of your lot area. Here are some things to consider:
- Include:
- The main part of your land
- Any private driveways
- Gardens or yards within your property lines
- Exclude:
- Public roads or sidewalks
- Any land outside your property boundaries
Understanding what to include and exclude is crucial. It helps you get an accurate lot area. And this, in turn, helps you calculate your FAR correctly.
So there you have it. Determining your lot area is the first step in measuring your Floor Area Ratio. It’s like finding the foundation for your building project. Get this right, and you’re on your way to a successful project.
Far Calculation Methods
Hey friends, today we’ll explore how to measure the Floor Area Ratio (FAR) for building projects. It’s an important step in planning and designing buildings. Let’s dive into the different FAR calculation methods. We’ll keep it simple and easy to follow. You’ll be an expert in no time!
Basic Formula
First things first, let’s talk about the basic formula to calculate FAR. This is the foundation of understanding how much space you can use for your building.
Here’s the basic formula:
FAR = Total Building Floor Area / Total Plot Area
Let’s break it down:
- Total Building Floor Area: This includes the sum of all the floors in your building.
- Total Plot Area: This is the area of the land on which your building sits.
For example, if you have a plot area of 1,000 square meters and your building has a total floor area of 2,000 square meters, your FAR would be 2. Easy, right?
Advanced Considerations
Now that you know the basic formula, let’s look at some advanced considerations. These are additional factors that might affect your FAR calculation.
Here are a few points to consider:
- Zoning Regulations: Different areas have different rules. Check your local zoning laws.
- Exclusions: Some areas, like basements or parking, might not count towards the total floor area.
- Height Restrictions: Some zones have limits on how tall your building can be. This can impact your FAR.
It’s always a good idea to consult with a local architect or urban planner. They can help you navigate these advanced considerations. Trust me, it saves a lot of headaches!
I remember when I first calculated FAR for a project, I missed a zoning rule. It was a small oversight but it caused delays. Learning from that, I always double-check now. You should too!
So, there you have it. The basic formula and advanced considerations for calculating FAR. Keep these points in mind, and you’ll be well on your way to planning your next building project with confidence.

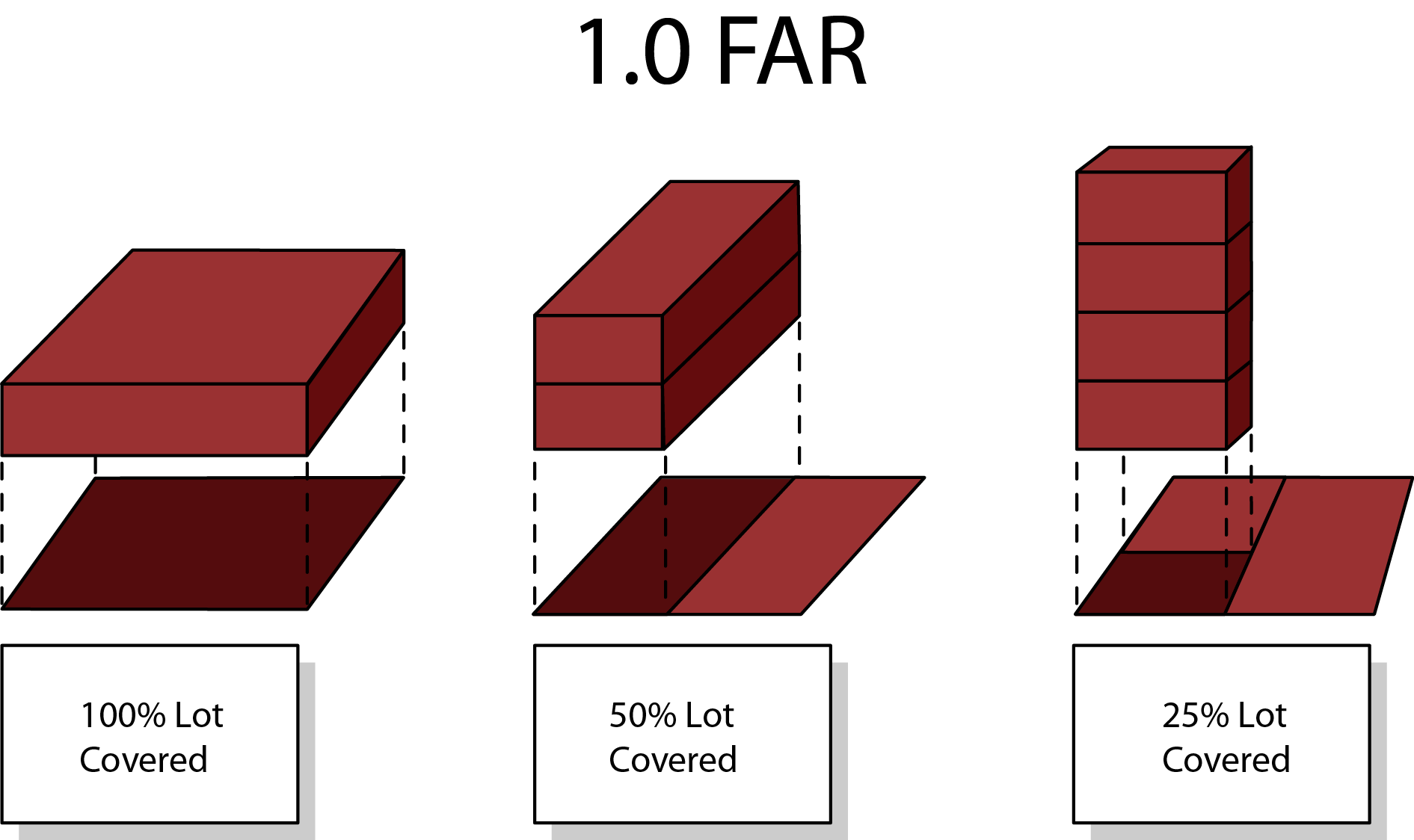
Credit: www.wallstreetprep.com
Practical Examples
Hey friends, today I’ll show you how to measure Floor Area Ratio (FAR) for building projects using practical examples. It can seem a bit tricky at first, but once you see how it’s done, it becomes much easier. Let’s dive in!
Residential Projects
Let’s start with residential projects. Imagine you have a plot of land that measures 10,000 square feet. The local zoning code allows a FAR of 1.5 for residential areas. So, how do you calculate the maximum floor area you can build?
It’s simple. You multiply the size of the plot by the FAR:
In our case:
Floor Area = 10,000 sq ft x 1.5 = 15,000 sq ft
This means you can build up to 15,000 square feet of floor space. This could be spread over multiple floors. For example, you could have:
- 5,000 sq ft on the ground floor
- 5,000 sq ft on the first floor
- 5,000 sq ft on the second floor
Easy, right? Now let’s look at another example.
Commercial Developments
Commercial developments work in a similar way. Suppose you have a commercial plot of land that is 20,000 square feet. The zoning code for this area allows a FAR of 2.0. Here’s how you calculate it:
Again, you multiply the plot size by the FAR:
So in this case:
Floor Area = 20,000 sq ft x 2.0 = 40,000 sq ft
This means you can build up to 40,000 square feet of floor space. You might decide to distribute this space as follows:
- 10,000 sq ft on the ground floor
- 10,000 sq ft on the first floor
- 10,000 sq ft on the second floor
- 10,000 sq ft on the third floor
That’s how it’s done! Once you get the hang of it, calculating FAR becomes second nature.
Remember, always check the local zoning codes for the specific FAR regulations in your area. And if you’re ever in doubt, consult with a professional. Happy building!
Impact On Design And Construction
Understanding Floor Area Ratio (FAR) is crucial for any building project. FAR impacts both design and construction. This ratio influences the overall layout, space utilization, and architectural flexibility. Knowing how to measure FAR helps in making informed decisions.
Architectural Flexibility
A higher FAR offers greater architectural flexibility. Designers can create multi-story buildings. This allows for creative freedom. Architects can experiment with different design styles. A higher FAR can accommodate more amenities. This could include recreational areas or rooftop gardens. It provides more room for innovative features.
Space Utilization
FAR directly affects space utilization. A high FAR maximizes usable space. This is vital for urban projects. Efficient space utilization can lead to better project outcomes. It ensures every square foot is used wisely. Proper planning ensures that the building meets all needs. It can also reduce construction costs. Efficient use of space means less waste.
Understanding FAR helps in achieving a balance. This balance is between density and functionality. Proper space utilization is key to a successful building project.
Common Mistakes To Avoid
Understanding how to measure Floor Area Ratio (FAR) is crucial for building projects. Mistakes in this process can lead to project delays and increased costs. Avoiding common errors ensures compliance with local regulations and efficient use of space.
Misinterpretation Of Codes
Local building codes can be complex and confusing. Misinterpreting these codes often leads to incorrect FAR calculations. Always double-check the regulations specific to your area. Consulting with a professional can help avoid misunderstandings.
Inaccurate Measurements
Accurate measurements are essential for correct FAR calculations. Small errors can significantly impact your project. Use reliable tools and double-check your measurements. Ensuring precision saves time and resources in the long run.
Expert Tips For Accurate Measurement
Accurately measuring the Floor Area Ratio (FAR) is crucial for building projects. FAR determines the relationship between the total floor area of a building and the size of the plot. Incorrect measurements can lead to legal issues or wasted resources. Here are some expert tips to ensure your FAR calculations are precise.
Using Technology
Modern technology offers tools that simplify FAR calculations. Software like AutoCAD or Revit can provide detailed measurements. These tools help in creating accurate building designs. They also help in ensuring that the FAR complies with local regulations. Drones equipped with measurement tools can survey large plots quickly. This reduces the risk of human error.
Consulting Professionals
Consulting professionals is another way to ensure accurate FAR measurement. Architects and surveyors have the expertise needed for precise calculations. They are familiar with local building codes and regulations. Their experience can help you avoid common mistakes. Hiring a professional can save time and reduce stress. They can also offer advice on how to optimize your building’s design.
Credit: www.multifamilyrefinance.com
Frequently Asked Questions
How To Calculate Gfa Of A Building?
Calculate GFA by measuring the total area within the building’s exterior walls, including all floors. Exclude non-habitable spaces like parking, mechanical rooms, and exterior areas.
What Is The Difference Between Gfa And Far?
GFA (Gross Floor Area) measures the total floor area inside a building. FAR (Floor Area Ratio) is the ratio of a building’s total floor area to its plot size.
How Do You Measure The Floor Area Of A Building?
Measure the floor area by multiplying the length and width of each room. Add the areas of all rooms together.
How To Calculate Land To Building Ratio?
Calculate the land to building ratio by dividing the total land area by the building’s footprint area. Ensure both measurements are in the same units.
Conclusion
Calculating Floor Area Ratio (FAR) is essential for building projects. It helps in understanding space utilization. Always refer to local codes for accuracy. Follow the steps we’ve discussed. This ensures your project meets regulations. Accurate FAR aids in better planning.
It avoids legal issues. Stay informed and measure carefully. This brings success to your building projects. Happy building!

Rakib Sarwar is a seasoned professional blogger, writer, and digital marketer with over 12 years of experience in freelance writing and niche website development on Upwork. In addition to his expertise in content creation and online marketing, Rakib is a registered pharmacist. Currently, he works in the IT Division of Sonali Bank PLC, where he combines his diverse skill set to excel in his career.
