3D modeling plays a vital role in engineering measurement. It enhances accuracy and efficiency.
In the world of engineering, precision is key. Engineers rely on accurate measurements to design and build structures. 3D modeling has revolutionized this process. It allows for detailed and exact representations of objects. Engineers can now visualize and test designs before construction begins.
This technology reduces errors and saves time. It also helps in detecting potential issues early. By using 3D models, engineers can ensure their measurements are spot on. This leads to better outcomes and higher quality projects.
Introduction To 3d Modeling
Hey there! Today, we’re diving into a fascinating topic: 3D Modeling in Engineering Measurement. If you’re curious about how engineers create accurate and detailed models, then you’re in the right place. Let’s start with an introduction to 3D modeling.
Historical Background
First, let’s take a step back in time. 3D modeling wasn’t always as advanced as it is today. Decades ago, engineers relied on 2D drawings and physical prototypes. These methods were time-consuming and often less accurate. But with the advent of computers, everything changed. Engineers began using Computer-Aided Design (CAD) software. This software made it possible to create detailed 3D models on a computer screen. Think of it as drawing, but in three dimensions. This leap from 2D to 3D was like moving from black-and-white TV to color. It was a game-changer for engineering.
Importance In Modern Engineering
Now, let’s talk about why 3D modeling is so important today. In modern engineering, precision is key. Even a tiny mistake can lead to big problems. Here’s where 3D modeling comes in handy:
- Accuracy: 3D models are incredibly detailed. They show every angle and dimension of an object. This means fewer mistakes and more accurate measurements.
- Visualization: Engineers can see how a part will look and fit in the real world. This helps in identifying potential issues early.
- Efficiency: Creating a 3D model is faster than building a physical prototype. This speeds up the design process.
- Collaboration: Teams can easily share and work on 3D models. This is especially useful in large projects where multiple people are involved.
Imagine you’re building a car. With 3D modeling, you can see how each part fits together. You can even simulate how the car will perform under different conditions. It’s like having a crystal ball that shows you the future of your design. Cool, right?
In conclusion, 3D modeling is a powerful tool in modern engineering. It combines accuracy, efficiency, and visualization to create better designs. So, the next time you see a perfectly engineered product, remember that 3D modeling played a big role in making it happen.
Stay tuned for more insights into the world of engineering measurement. Until next time!

Credit: guandiaocnc.en.made-in-china.com
Basics Of 3d Modeling
Hey friends, today I’ll show you the basics of 3D modeling in engineering measurement. 3D modeling is a way to create a digital representation of an object. Think of it like building with LEGO, but on a computer. This technology helps engineers design, measure, and visualize objects before making them in real life. Let’s dive into the core concepts and common tools used in 3D modeling.
Core Concepts
First, let’s cover the core concepts of 3D modeling. These are the building blocks that you need to understand:
- Vertices: Points in 3D space that define the shape of an object.
- Edges: Lines connecting vertices, forming the skeleton of the object.
- Faces: Flat surfaces enclosed by edges, giving the object its form.
- Meshes: Collections of vertices, edges, and faces that make up the 3D model.
These elements work together to create detailed and accurate models. Engineers use these models to measure dimensions, test designs, and ensure everything fits perfectly before actual production.
Common Tools And Software
Now, let’s talk about the tools and software that make 3D modeling possible. There are several popular options, each with its own strengths:
- AutoCAD: This is like the Swiss Army knife of 3D modeling. It’s great for precise measurements and detailed designs.
- SolidWorks: Engineers love this one for creating complex mechanical parts and assemblies. It’s like having a high-tech toolbox at your fingertips.
- Blender: This is a favorite among designers and animators. It’s free and perfect for creative projects.
- TinkerCAD: If you’re new to 3D modeling, this is a great starting point. It’s simple and easy to use, like drawing with digital clay.
These tools help engineers create detailed models quickly and accurately. They also allow for easy modifications, so if something doesn’t look right, you can fix it without starting from scratch. It’s like editing a document on your computer – make a change, hit save, and you’re good to go.
I recently tried using AutoCAD for a project. I was amazed at how precise my measurements were. It felt like I had a digital ruler and protractor in my hand. The good news? You can achieve the same results with a bit of practice.
Remember, the key to mastering 3D modeling is practice and patience. Start with simple shapes, learn the basics, and soon you’ll be creating complex models like a pro. Happy modeling!
Applications In Engineering Measurement
3D modeling plays a critical role in engineering measurement. It offers precise and detailed visualizations. These visualizations help engineers make accurate decisions. They also improve the overall efficiency of the engineering process.
Accuracy Enhancement
3D modeling enhances measurement accuracy. Engineers can create exact models of their projects. These models allow for precise measurements. Even the smallest details are captured. This reduces errors and improves the quality of the final product.
Streamlining Processes
3D modeling helps streamline engineering processes. It saves time by providing clear visual guides. Engineers can easily identify potential issues. This early detection helps prevent costly mistakes. The overall workflow becomes smoother and more efficient.
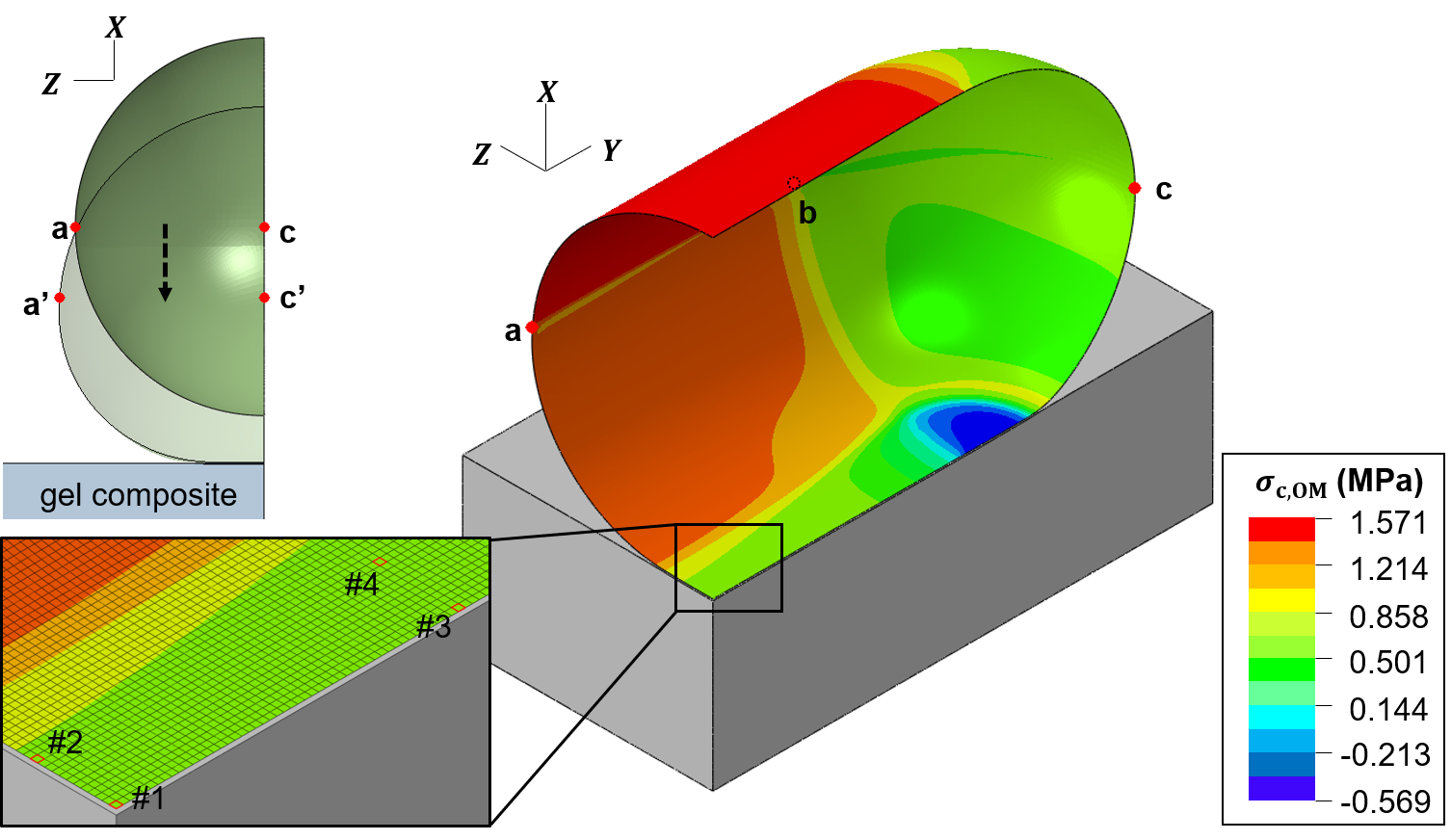
Credit: chaos.utexas.edu
Technological Advancements
Hey friends, today let’s dive into the exciting world of 3D modeling in engineering measurement. Technology has come a long way, and it’s making things easier and more precise in many fields. Engineering measurement is no exception. With the help of 3D modeling, engineers can now measure and analyze structures and components with incredible accuracy. But what are the technological advancements that have made this possible? Let’s explore!
Innovative Techniques
One of the coolest things about 3D modeling is the new techniques that have emerged. These techniques have changed how engineers work. For example:
- Laser Scanning: This technique uses lasers to capture the shape of objects. It’s like taking a high-tech snapshot, but in 3D. Engineers can then use these scans to create detailed models.
- Photogrammetry: This involves taking lots of photos from different angles. Software then stitches these photos together to create a 3D model. It’s kind of like a puzzle, but with pictures!
- CT Scanning: Just like in medical imaging, CT scans can be used in engineering. They provide a look inside objects without taking them apart.
Future Trends
What’s next for 3D modeling in engineering measurement? The future looks bright with several trends on the horizon:
- AI Integration: Artificial intelligence will play a big role. AI can help analyze data faster and more accurately.
- Enhanced VR and AR: Virtual Reality (VR) and Augmented Reality (AR) will become more common. Imagine being able to walk through a 3D model and see everything up close. Amazing, right?
- Improved Accessibility: As technology becomes cheaper and easier to use, more people will have access to these tools. This means even small engineering firms can benefit.
These trends will make 3D modeling even more useful and widespread in the future. Exciting times ahead!
So, friends, 3D modeling is not just a fancy tool. It’s a game-changer in engineering measurement. Whether it’s using innovative techniques or looking forward to future trends, 3D modeling is here to stay. And it’s making things easier, faster, and more accurate for engineers everywhere. Stay tuned for more updates on this fascinating topic!
Case Studies
Case studies provide real-life examples of how 3D modeling impacts engineering measurement. These examples highlight the practical applications and benefits of this technology. Let’s explore some real-world examples and success stories in this field.
Real-world Examples
In the automotive industry, 3D modeling helps in designing complex parts. Engineers use 3D models to ensure precision and accuracy. This reduces errors during the manufacturing process. For example, a leading car manufacturer improved their assembly line using 3D models. They detected design flaws early and saved time and costs.
Another example comes from the aerospace sector. Aircraft designers use 3D modeling to create detailed models of aircraft components. This ensures that every part fits perfectly, improving safety and performance. An aerospace company used 3D models to simulate stress tests. This helped them identify weak points and enhance the durability of their aircraft.
Success Stories
Construction companies benefit greatly from 3D modeling. A construction firm used 3D models to plan a large infrastructure project. This allowed them to visualize the entire structure before building. They identified potential issues and made necessary adjustments. As a result, the project was completed on time and within budget.
In the field of healthcare, 3D modeling has also shown its value. Surgeons use 3D models to plan complex surgeries. This allows them to practice and prepare in advance. A hospital reported a significant increase in successful surgeries after adopting 3D modeling. Patients experienced better outcomes and faster recovery times.
These cases demonstrate the crucial role of 3D modeling in engineering measurement. Real-world examples and success stories highlight its impact on various industries. The precision and efficiency offered by 3D modeling make it a valuable tool in modern engineering.
Challenges And Limitations
3D modeling in engineering measurement offers many benefits. Yet, it also brings challenges and limitations. Engineers often face technical issues and cost concerns. Understanding these challenges helps in better planning and execution.
Technical Hurdles
Technical hurdles are common in 3D modeling. High accuracy is hard to achieve. Complex shapes and surfaces pose additional difficulties. Software compatibility can also be a problem. Not all software tools work well together. Data transfer between different platforms may result in errors.
Another issue is the learning curve. Engineers need time to master new tools. This can slow down projects. Hardware limitations are also a concern. High-end computers are often required for detailed models. Not every engineering firm can afford these.
Cost Implications
3D modeling can be expensive. Software licenses often come with high costs. Regular updates and maintenance add to these expenses. Training staff on new software also requires investment. This can be a burden for smaller firms.
Hardware upgrades can further increase costs. High-performance computers and storage are necessary. These upgrades are not cheap. Outsourcing 3D modeling services is another option. But it can lead to higher overall project costs.
Understanding these challenges helps engineers plan better. They can choose the right tools and allocate resources wisely.
Industry Adoption
Hey friends, today we’re diving into something pretty cool – the role of 3D modeling in engineering measurement. This tech is transforming how engineers work. But how widely is it being adopted? Let’s break it down.
Current Usage
So, where are we now? 3D modeling is catching on fast. Engineers use it to create detailed designs. These designs are used for buildings, machines, and even bridges. It’s like drawing a blueprint, but way more detailed.
Why do engineers love it?
- Accuracy: 3D models are super precise. This means fewer mistakes.
- Visualization: You can see what you’re building before you start. Kind of like seeing a movie trailer before you watch the whole film.
- Time-Saving: It speeds up the design process. Imagine writing with a computer instead of a typewriter.
Many industries are on board. Construction, automotive, and aerospace are just a few examples. They all use 3D modeling to make their work easier and better.
Adoption Barriers
But not everyone is using 3D modeling yet. Why? Let’s talk about some barriers.
- Cost: The software can be pricey. Small companies might struggle to afford it.
- Training: Learning new tech takes time. Engineers need to be trained, and this can be a big investment.
- Resistance to Change: Some people are set in their ways. They might not want to switch from old methods.
Think about it. Switching to 3D modeling is like moving from a flip phone to a smartphone. It’s better, but it takes some getting used to.
I remember when I first tried 3D modeling. It seemed tough at first, like learning to ride a bike. But once I got the hang of it, it became second nature. And the good news? The benefits far outweigh the challenges.
So, will 3D modeling become the norm? Time will tell. But one thing is sure. Its potential is huge, and industries that embrace it will likely see big gains.
Credit: www.3deservice.com
Future Of 3d Modeling In Engineering
Hey friends, today we’re diving into something super exciting – the future of 3D modeling in engineering. You know how engineers are always looking for the best tools to measure and design stuff? Well, 3D modeling is like their magic wand. But what does the future hold for this amazing tech? Let’s break it down.
Predicted Developments
So, what’s next for 3D modeling? Experts say there are some cool developments on the horizon. First up, better software. Imagine using a program that’s as easy as drawing on paper, but it creates 3D models. Engineers will love it because it saves time and reduces mistakes.
Then, there’s faster processing. Right now, rendering 3D models can take ages. But soon, new tech will make it super quick. This means engineers can work faster and see results instantly.
And let’s not forget virtual reality (VR). Picture this: engineers putting on VR headsets and walking around their designs. They can spot issues before building anything. It’s like having a crystal ball for construction projects.
Potential Impact
What does all this mean for the engineering world? A lot, actually. Let’s break it down.
- Accuracy: 3D models will be more precise. This means fewer errors and better structures.
- Efficiency: Faster processing saves time. Engineers can complete projects quicker.
- Cost-Effective: Spotting issues early means less money spent fixing mistakes later.
- Collaboration: With VR, teams can work together from anywhere. It’s like having a meeting room in the cloud.
Personally, I recently asked an engineer friend about these changes. He said he’s excited about VR. He imagines showing clients around a virtual building. They can see exactly what they’re getting. And if they want changes? Easy. Just tweak the model in real-time. How cool is that?
| Development | Impact |
|---|---|
| Better Software | More user-friendly, less errors |
| Faster Processing | Quicker project completion |
| Virtual Reality | Enhanced collaboration, early issue detection |
The future of 3D modeling in engineering looks bright. With these advancements, engineers will create more accurate, efficient, and cost-effective designs. So, keep an eye out for these changes. They’re set to make a big splash in the engineering world!
Frequently Asked Questions
Why Is 3d Modeling Important In Engineering?
3D modeling is crucial in engineering for visualizing designs, detecting flaws, and improving accuracy. It enhances communication, reduces costs, and speeds up project timelines.
What Is 3d Modelling In Mechanical Engineering?
3D modeling in mechanical engineering involves creating a digital representation of a physical object. Engineers use specialized software to design, analyze, and simulate components. This process enhances visualization, improves accuracy, and speeds up the development cycle. 3D models are essential for prototyping, testing, and manufacturing.
What Is The Purpose Of 3d Modeling?
3D modeling creates digital representations of objects, enhancing visualization, design accuracy, and prototypes. It aids in various fields like architecture, gaming, and manufacturing.
Why Are You Interested In Engineering Design And 3d Modelling?
I love engineering design and 3D modelling because they blend creativity and technical skills. Solving complex problems and bringing ideas to life excites me.
Conclusion
3D modeling greatly enhances engineering measurement accuracy. Engineers visualize projects clearly. This technology reduces errors and saves time. Designs become more precise and efficient. Adopting 3D modeling is essential for modern engineering. It bridges the gap between ideas and reality.
Stay ahead by incorporating 3D models in your workflow. Embrace this tool for better results.

Rakib Sarwar is a seasoned professional blogger, writer, and digital marketer with over 12 years of experience in freelance writing and niche website development on Upwork. In addition to his expertise in content creation and online marketing, Rakib is a registered pharmacist. Currently, he works in the IT Division of Sonali Bank PLC, where he combines his diverse skill set to excel in his career.
